We aim to help our clients get the most out of their cloud computing experience. This document applies to all cloud computing platforms, private or public. Cloud desktop (VDI) performance depends heavily on the VDI resources and network connectivity.
If a client is experiencing poor VDI performance, this is due to one or a combination of the following points below, and in most cases, the reason for poor performance can be self-diagnosed.
For Example:
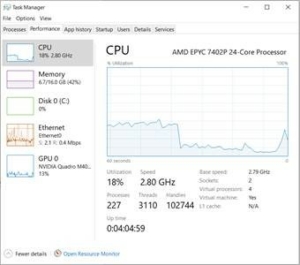
1. If the VDI resources are low, you can view this in Microsoft Windows by selecting the Task Manager and the Performance tab (see below) and seeing your resource utilization. Anything above 85% is considered high, and a resource upgrade is recommended.
2. If the LAN or the WAN is poor, this will require a more thorough assessment by an A2000 engineer; however, you can run a simple 5 minute test utilizing the following tool to determine this.
The test requires you to run it directly from a local PC connected via a wire, NOT over WIFI, and NOT from your A2000 VDI, and from where you desire to test the quality of the LAN or WAN. See below.
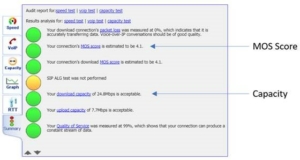
Mean Opinion Score (MOS) is a measure used in the domain of Quality of Experience and telecommunications engineering
How to interpret your results?
If your MOS score is below 4, your LAN or WAN or both are poor quality or defective – Your office network hardware, service provider connection one, or both are over-utilized, misconfigured, require an upgrade, or are faulty.
Analyze your download and upload speeds; if they are below our recommendation, you should consider upgrading your service provider connection. We recommend minimum downloads and uploads of 10 Mbps and 5 Mbps for each VDI user. For example, a 5-user office operating over the Internet will require a minimum of 50 Mbps download and 25 Mbps upload as minimum capacity.
3. Other recommendations:
All these best practices will optimize your performance, improve your security and enhance your cloud computing experience.
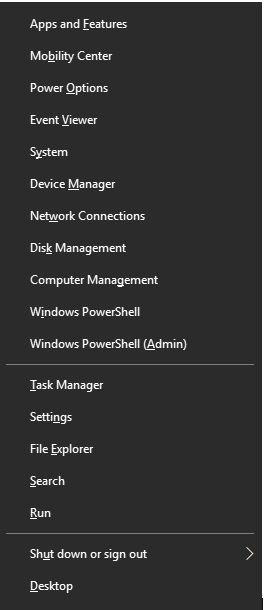
1. Press Windows Key + X combination to see the following menu.
2. Click System
3. In the search field type advance system
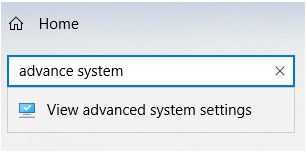
4. Click View advanced system settings
5. Under the advanced tab, under performance click settings
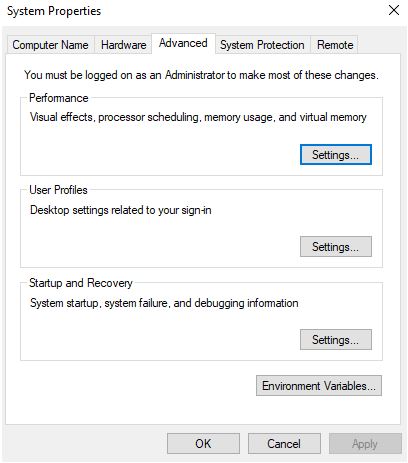
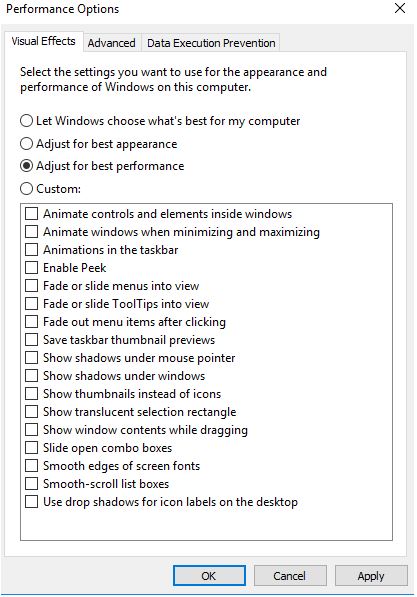
6. Click adjust for best performance and click ok
Consider the following best practices for managing views in your project.
|
Uploaded
Failed
|
 |
Customer Service Available 24/7 at
(800) 238-2621
Get news from Advance2000 in your inbox.